
The Evolution of General Aviation Aircraft: What’s Changed Over the Years?
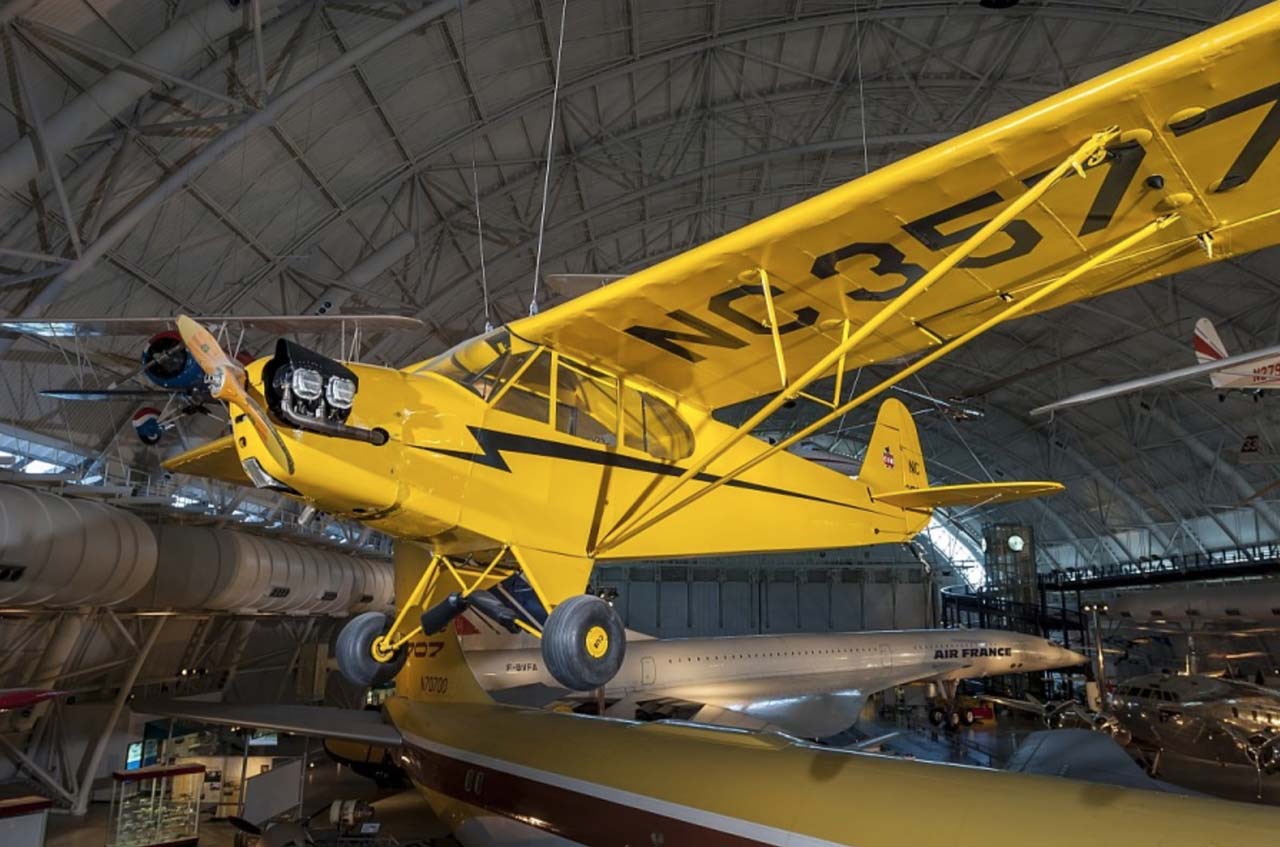
Piper J-3 Cub: distinctive yellow, high-wing light monoplane with tailwheel; trainer and sport aviation; Continental A-65, 65 hp engine. Photo courtesy of National Air and
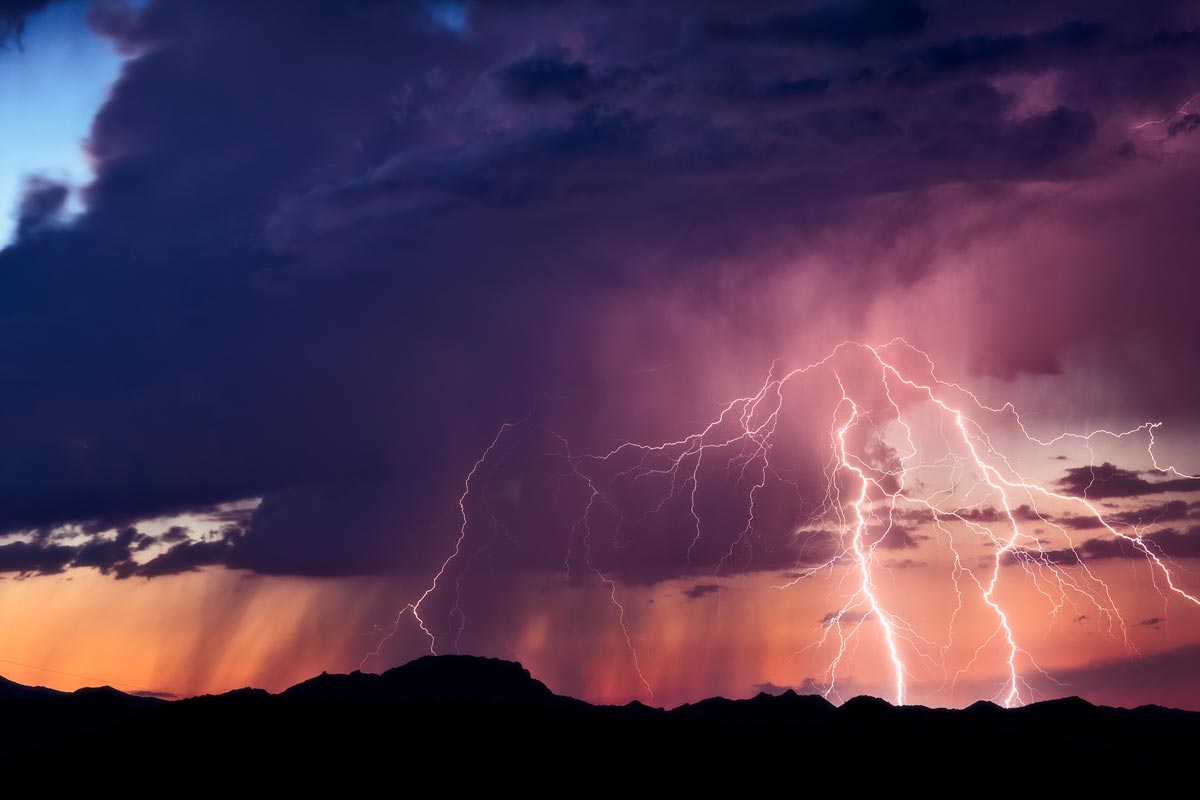

Last night, the Lower Mainland experienced a major thunderstorm accompanied by lightning. This event underscores the challenges aircraft encounter in adverse weather conditions. Lightning strikes represent a significant risk to aviation safety, prompting a closer look at how aircraft are designed to withstand such occurrences.
To protect passengers and crew, aircraft are designed with materials and technologies that can withstand lightning strikes. This includes using conductive materials like aluminum and composites, and installing Lightning Protection Systems (LPS) consisting of static dischargers, lightning receptors, and grounding mechanisms.
These systems help to dissipate the energy from lightning strikes and prevent damage to critical components. Additionally, aircraft undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand lightning strikes before being certified for operation. Overall, aircraft are built with safety measures to mitigate the risks posed by lightning strikes and ensure the safety of those on board.
Aircraft are built using materials known for their high electrical conductivity, primarily aluminum alloys and composite materials reinforced with conductive fibers. These materials are chosen for their ability to facilitate lightning currents flow along the aircraft’s surface. By allowing the lightning energy to travel smoothly across the aircraft’s exterior, these conductive materials help dissipate the electrical charge, thus minimizing the risk of damage.
Moreover, conductive coatings or paints are applied to the aircraft’s exterior surfaces to enhance conductivity and ensure efficient lightning energy discharge. These coatings create a seamless pathway for the lightning discharge, effectively guiding the electrical current away from critical components and reducing potential harm. By integrating these conductive materials and coatings into the aircraft’s construction, manufacturers bolster the aircraft’s resilience against lightning strikes, enhancing overall safety for passengers and crew alike.
Modern aircraft have sophisticated Lightning Protection Systems (LPS) comprising several components designed to intercept, conduct, and safely discharge lightning strikes. These systems typically include:
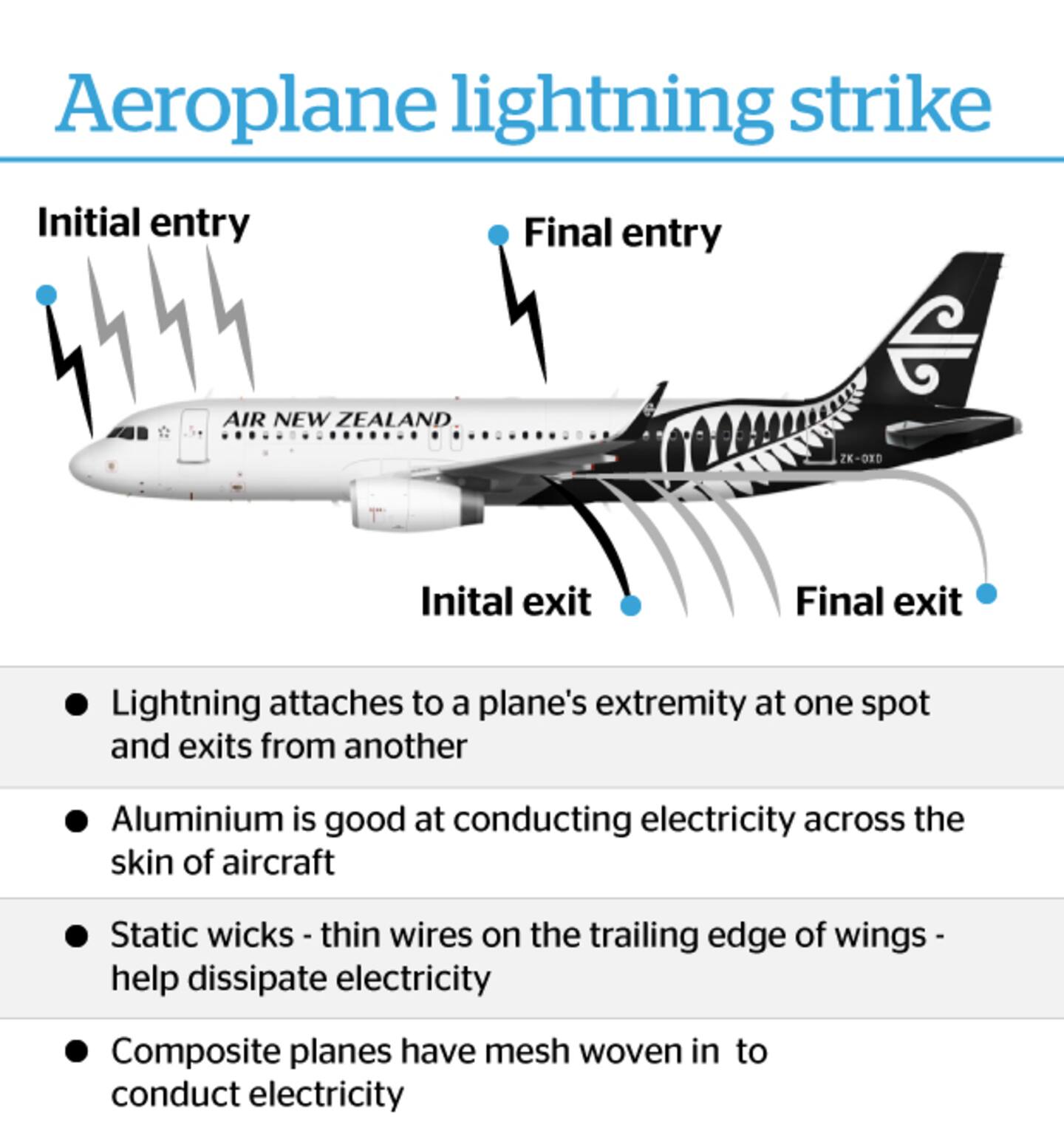
The aluminium used on most commercial aircraft conducts electricity and allows lightning to pass across its skin. The current usually exits the aircraft at the tail. Read more here.
Image courtesy of nzherald.co.nz
Aircraft systems are designed with redundancy to ensure continued operation and structural integrity during lightning strikes. Critical components such as flight control surfaces, avionics, and electrical systems are often duplicated or protected by backup systems to maintain functionality. Furthermore, aircraft structures undergo rigorous testing and analysis to withstand the mechanical stresses induced by lightning, including aerodynamic loads and thermal effects.
The Boeing 737 is equipped with a Lightning Protection System (LPS) to mitigate the risks of lightning strikes. This system comprises various components designed to intercept, conduct, and safely dissipate lightning’s electrical energy. Click here for more.
Before an aircraft is certified for commercial operation, it must undergo comprehensive lightning testing and certification procedures mandated by aviation regulatory authorities such as the Transport Canada Civil Aviation (TCCA) or the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). These tests simulate lightning strikes using high-energy discharges and evaluate the aircraft’s ability to withstand and dissipate the resulting electrical currents without sustaining critical damage. Compliance with stringent certification standards ensures aircraft are resilient to lightning strikes under real-world operating conditions.
In conclusion, aircraft designed and engineered to withstand lightning strikes represent a testament to the aerospace industry’s commitment to safety and innovation. By integrating conductive materials, lightning protection systems, redundant systems, and rigorous testing protocols, aircraft manufacturers ensure the resilience and reliability of modern aircraft in the face of nature’s formidable forces. By continuously advancing technology and adhering to stringent safety standards, the aviation industry endeavors to minimize the risks posed by lightning strikes and uphold the highest standards of passenger and crew safety.

Climb aboard this unique experience; you can book a 30-minute Introductory Flying Lesson with one of our qualified Flight Instructors and discover what flying is all about! Click for more info!

Piper J-3 Cub: distinctive yellow, high-wing light monoplane with tailwheel; trainer and sport aviation; Continental A-65, 65 hp engine. Photo courtesy of National Air and
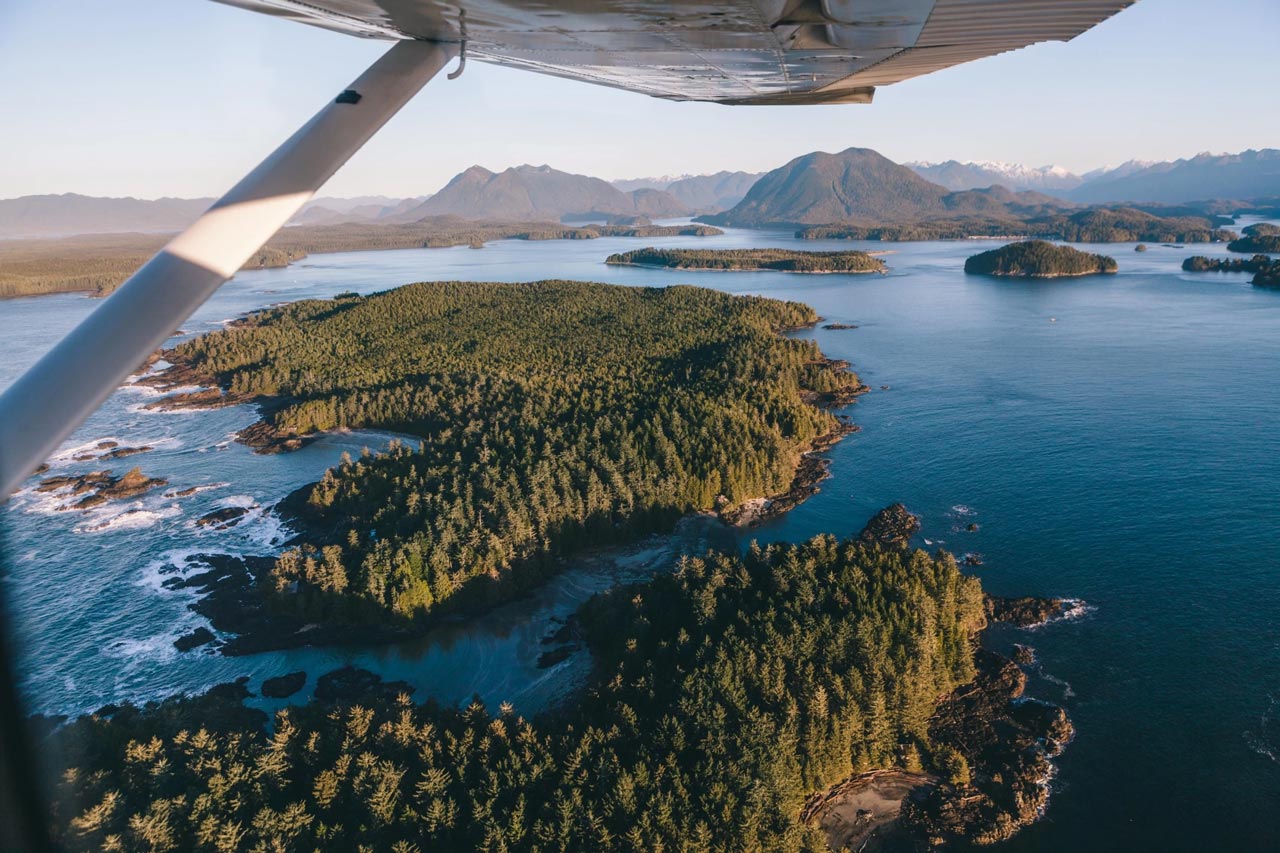

Photo of Clayoquot Sound by Jordan Giesbrecht courtesy of Tourism Tofino. Scenic Flights in North America offer more than just impressive views — they offer

You lift off from a small airport, climb above the trees, and head toward the mountains. Below, rivers wind through thick forests, and narrow gravel


Historical Background Boundary Bay Airport was constructed in 1941 as part of the British Commonwealth Air Training Plan, one of the largest aviation training programs

Who Are Canadian Snowbirds? Officially known as the Canadian Forces Snowbirds (431 Air Demonstration Squadron), they’re more than just an air show attraction. The Snowbirds